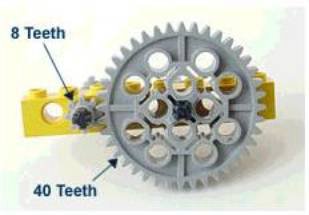
Here is a picture of one of the Lego sensors known as an Angle Sensor or a Rotation Sensor. Notice the hole in it. That's where an axle fits.
Here is how it works. The sensor senses the rotating axle. It counts in little steps a sixteenth at a time. When the sensor port displays 16 it is telling you that the axle rotated one full revolution.
So to make the sensor useful to all of us future engineers, we can measure the distance we want to go by using the "View" feature on the RCX. Then in Robolab, we enter the numerical value we took from View and enter that value into numerical input on the sensor icon in the code. Small adjustments are made after some trial and error for that mission. This becomes a very acurate method to measure distance.
The Angle Sensor gets that name versus Rotation Sensor from this: Since the sensor counts in small bits at time and those bits are equal and there are sixteen of them, people who know these characteristics divide the 360 degrees of rotation by the sixteen bits and now can measure angles. Each increment of that division problem yields 22.5 degrees- Very helpful when using an Angle Sensor on a motor for an arm. Two counts is 45 degrees. Four makes 90 degrees and so on.
Does this give you any ideas?- if so post a comment. Use rules of regular English like Capital Letters! These posts are getting sloppy. This is a forum for intellectual exchange between students and teachers. It is not a place for AOL lingo. I want your comments- not slang.
Keep in mind this is the WorldWideWeb- anyone, anywhere may read this. Your potential audience is anyone in the world with internet connectivity. You are known only by what and how you write. If you write nonsense- well, there you go. BUT! So many of you write such execellent comments. We get very good feedback about your participation. That makes me so proud of all of you!
Thanks.